Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is defined as the specialty of dentistry that includes the diagnosis, surgical, and adjunctive treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects involving the functional and esthetic aspects of the bone and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. These include complex tooth removal, surgical removal of wisdom teeth and impacted teeth, dental implants and related bone grafts, sinus lift surgery, temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) treatment, cleft lip palate, facial trauma or fracture, and orthopedic surgery of the jaw bone. In addition, they will also do biopsy and removal for jaw bone cysts, oral tumors, and tissue hyperplasia.
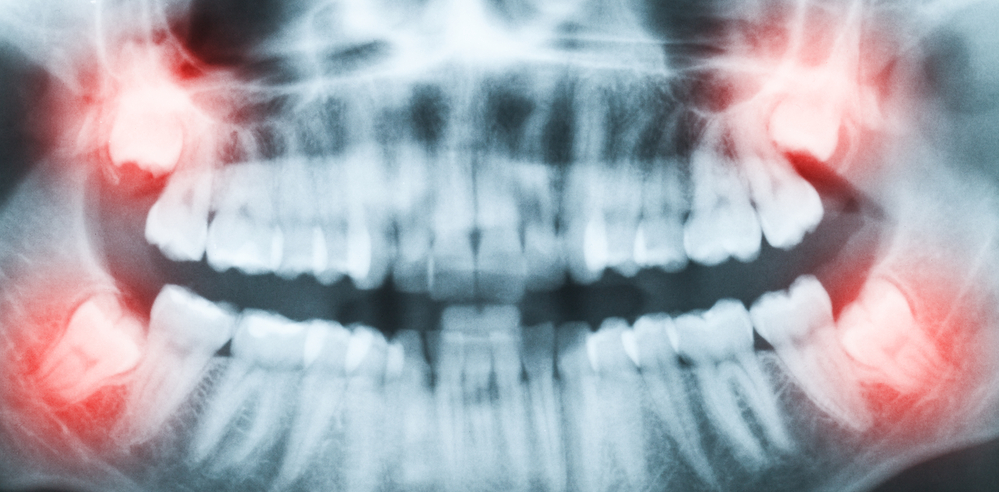
Wisdom Tooth Extraction
 Wisdom teeth get their name because they are the last teeth to come in, around the time of young adulthood – the age when a person gains maturity and wisdom. Most permanent (adult) teeth come in by age 13. A few years later, between ages 17-25, your wisdom teeth usually push their way through your gums.
Wisdom teeth get their name because they are the last teeth to come in, around the time of young adulthood – the age when a person gains maturity and wisdom. Most permanent (adult) teeth come in by age 13. A few years later, between ages 17-25, your wisdom teeth usually push their way through your gums.
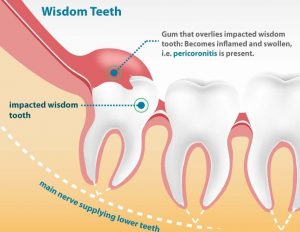
But sometimes wisdom teeth do not have enough room to come in, or are in the wrong position. These wisdom teeth are called “impacted” and may have to be removed.
Why and When are Wisdom Teeth Removed?
Wisdom teeth, are not needed for chewing and are often difficult to brush and floss. Your dentist may recommend the removal of your wisdom teeth in your late teens.
Potential problems with wisdom teeth
There are several problems that are seen commonly with wisdom teeth. These include:
- Infection when a wisdom tooth partially comes in through the gum and creates an opening where bacteria may enter. Pain, swelling and jaw stiffness may result.
- Damage nearby teeth caused by a wisdom tooth without enough room in the jaw or one that is poorly aligned.
- A fluid-filled sac (cyst) or tumor that forms on or near an impacted tooth, destroying surrounding bone or tooth roots.
Key Information
If you can maintain an ideal oral hygiene, or if the wisdom tooth is completely buried in the alveolar bone and does not grow out, or if the impacted wisdom tooth does not cause discomfort, you can observe the situation by regular inspections by dentists. If the impacted wisdom tooth is repeatedly causing discomfort which can lead to other problems, it may have to be removed.

